![Healthy Matters]() Pharmacist Tips | Dosages | Side effects
Pharmacist Tips | Dosages | Side effects![Healthy Matters]() Nutritionist Tips | Facts | Precautions
Nutritionist Tips | Facts | Precautions![Healthy Matters]() Practitioner Tips | Dosages | Side effects
Practitioner Tips | Dosages | Side effects![Healthy Matters]()
![Healthy Matters]()
Ultrasound: How It Works? Procedures & Costs in Hong Kong
4 min read
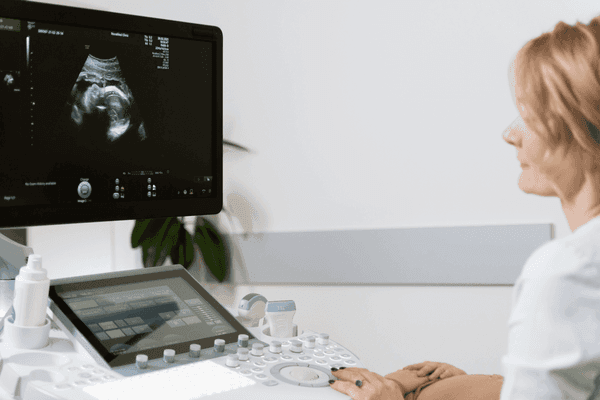
Ultrasound imaging is a non-invasive technique to form images of your body using sound waves. It can serve many purposes, including antenatal care (checking the fetus during pregnancy) and diagnosis of the cause of pain, swelling and inflammation. Scroll on to understand the procedure, applications and risks of ultrasound scanning.
What is ultrasound?
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than that humans can hear. The usage of ultrasound to produce images for diagnostic purposes is called medical ultrasonography, or simply sonography.
A typical ultrasound machine consists of a computer console, video monitor and piezoelectric transducer, which can transform electrical signals to sound waves and vice versa. The transducer can emit sound waves and detect the echoes (the reflected sound waves). Based on the time for the echoes to bounce back and the strength of the echoes, the computer then generates a 2D image to be displayed on the monitor.
Ultrasound has difficulty penetrating the bones and is obscured by gas. Therefore, it is not good for imaging organs filled with air (e.g. lungs) or surrounded by bones (e.g. brain). However, ultrasound does not produce ionizing radiation (unlike X-ray) and produces real-time images. Therefore, one of its most common applications is obstetric ultrasonography (ultrasound imaging of the fetus).
Common applications of ultrasound
Ultrasound is helpful for doctors to evaluate the cause of pain, swelling and inflammation as it can examine tissues under the skin.
External ultrasound scan can visualize and examine
- Muscles, ligaments and tendons
- Eyes
- Thyroid and parathyroid glands
- Breast
- Heart
- Abdomen
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Spleen
- Pancreas
- Kidneys
- Bladder
- Pelvis
- Uterus
- Ovaries
- Prostate gland
- Fetus
Internal ultrasound scan includes
- Transvaginal ultrasound scan
- Enables a closer look at the uterus and ovaries
- Transrectal ultrasound
- Enables a closer look at the prostate
Endoscopic ultrasound scan
- Examines stomach or esophagus
Doppler ultrasound
The Doppler effect is the frequency shift of a wave in relation to the observer whose relative position to the wave source is changing. When the wave source is moving towards the observer, each wave takes less time to reach the observer, resulting in an increase in frequency.
Doppler ultrasound utilizes this effect to measure the movement of tissues and body fluids, most commonly blood flow and renal perfusion. It is often used along echocardiogram (heart ultrasound) to have a more comprehensive examination of heart functions.
Other applications
- Bone sonometry
- Examine bone density to diagnose osteoporosis
- Guide biopsy
What should I expect from an ultrasound scan?
Before the ultrasound
Depending on the body parts being examined, the preparation could be completely different. You may need to fast for 8-12 hours before an abdominal ultrasound as food and drinks may interfere with the pictures. On the other hand, you may need to drink plenty of water and not urinate before a pelvic ultrasound (including fetal ultrasound in early stages) as ultrasound propagates better in water than in air.
You may be asked to remove clothing and jewelry from the area being examined and change into a gown, so you should wear loose clothing and leave your valuable jewelry at home.
During the ultrasound
Ultrasound scan is usually non-invasive/ minimally invasive and painless.
For external ultrasound scans, a water-based gel is applied to the skin over the body part being examined. This can prevent the air gap between the transducer and skin from blocking the ultrasound waves and provides lubrication. You may feel a bit cold when the gel is being applied.
For internal ultrasound scans, the transducer probe is inserted into your body through a natural opening. For endoscopic ultrasound scans, the transducer probe is attached to the endoscope and inserted into your body. You may experience discomfort and a sedative may be given for you to relax and stay still.
After the ultrasound
Ultrasound is very safe and usually does not have any aftereffects. In most cases, you can resume normal activities immediately after the gel is wiped off and you get dressed. If you were given a sedative, you may need to stay in the hospital for a few hours until it starts to wear off. You should not drive, operate machinery or consume alcohol while the sedative is still in effect.
The images of your ultrasound scan may need to be analyzed before your doctors can discuss the results with you and determine if treatment is needed.
Risks of ultrasound
Ultrasound, unlike imaging techniques like X-ray, does not emit ionizing radiation or require contrast agents. Therefore, it has minimal effects on your body.
External and internal ultrasound scans do not have any side effects. However, you must inform your doctors if you have allergies to the components of ultrasound gel (e.g. propylene glycol) or probe cover (e.g. latex).
Endoscopic ultrasounds may cause temporary side effects like a sore throat.
Costs of an ultrasound scan in Hong Kong
Ultrasound services are charged as private services in public hospitals. It costs between HK$1,000 and $6,210 per examination, depending on the body parts involved. Please be aware that in the public sector, waiting times can be extremely long.
In the private sector, you may visit any of the 13 private hospitals in Hong Kong, private clinics or imaging centers for an ultrasound scan. Based on our research, the cost can range from HK$800 to over $12,000 per examination, depending on the body parts involved. Please contact your service provider for the exact pricing and appointments.
Are ultrasounds covered by insurance?
Ultrasound scans are usually covered under outpatient radiology benefits when medically necessary. Most local standard plans have an annual diagnostic imaging limit and you may have to pay any outstanding balance out-of-pocket. Ultrasounds are usually covered in full by high-end international medical plans, with no sub-limits.
Obstetric ultrasounds are usually covered under your overall maternity benefit limit. In Hong Kong's private sector, it's a usual practice for OBGYNs to perform ultrasounds and bill at every prenatal and postnatal visit. Some insurers believe that not all ultrasounds are necessary and may impose a cap or limit their reimbursement to 3 to 4 scans per pregnancy. For more information, contact Alea's health insurance advisors.
Unlike several other imaging procedures, ultrasound does not use ionizing radiation or contrast chemicals. It has a negligible impact on your body.
Because sound waves do not travel well through air or bone, sonography cannot be used to image body parts that contain gas or are obscured by bone, such as the lungs or the brain. Ultrasound may also be unable to detect things buried deep inside the human body.
Depending on the sort of examination (external, internal or endoscopic) and the body parts examined, most ultrasound scans take around 20 to 40 minutes.
This article was independently written by Healthy Matters. It is informative only and not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. It should not be relied upon for specific medical advice.

Your health resource, made in Hong Kong
Healthy Matters is Hong Kong’s leading health resource. Our mission is to help you make better health decisions and take control of your health.
Our team of experts is committed to producing reliable health content that is accurate, engaging and relevant, to cover your health & wellness journey from prevention to treatment.
Whether you are looking for trusted information on health conditions, wellbeing or looking for the right doctor or service in Hong Kong, we’re here to help!
Your health matters. Begin your health journey with Healthy Matters today!